Using Python to create an ETL pipeline for data modeling with Apache Cassandra.
Summary
Create an Apache Cassandra database which can create queries on song play data for exploratory analysis.
- Processed the csv files from
event_datato create a single csv file that will be used for Apache Casssandra tables - Querying data through Apache Cassandra
- Created Cassandra Cluster and Keyspace
- Created a new table for each specific query
- Load data into each table from the aggregated file,
event_datafile_new.csv - Utilized Primary Key (includes Partition Key and Clustering columns) to query
ETL Pipeline Processing
- Combine all csv files from
event_datainto a denormalized dataset,event_datafile_new.csv - The image below is a screenshot of what the denormalized data appear like
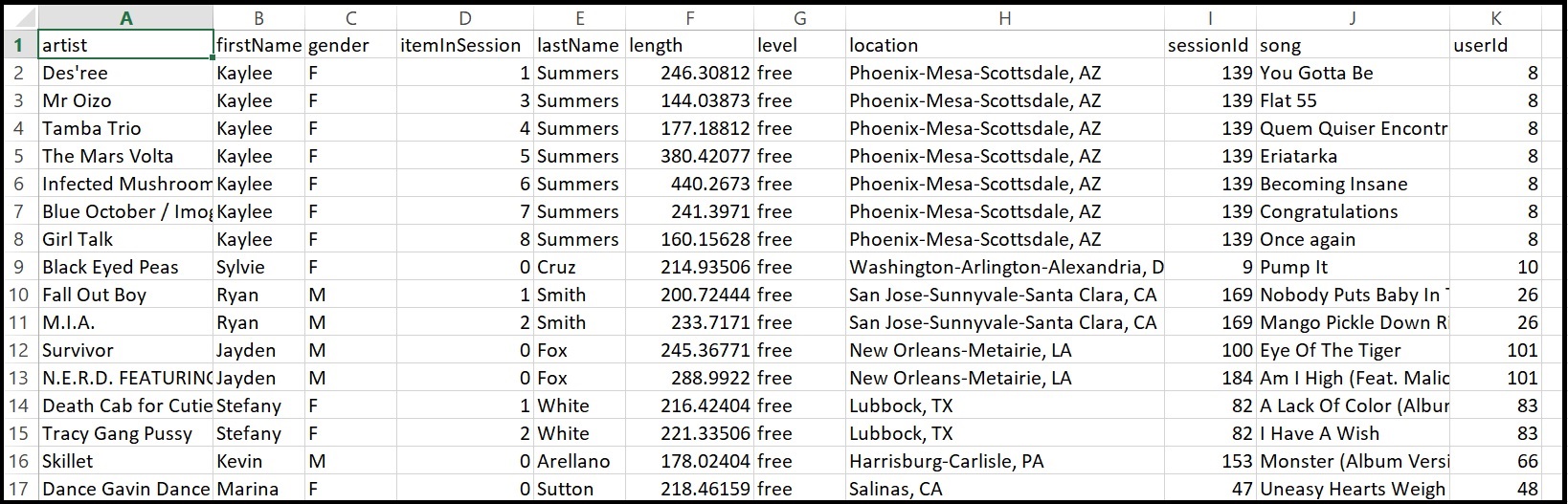
Data Modeling
- Created unique tables for each query
- The CREATE TABLE statement includes the appropriate datatype and unique names
- Table names reflect the query and the result it will generate
- Created one table per query, following the rules of Apache Cassandra
- Implemented PRIMARY KEY with a COMPOSITE Partition for both the CREATE and INSERT statements
- The SELECT statement does NOT use
ALLOW FILTERINGto generate the results
Primary Keys
- Apache Cassandra is a partition row store, the partition key determines which node a particular row is stored on
- The combination of the PARTITION KEY and CLUSTERING COLUMNS are used to uniquely identify each row
- With the Primary key (Partition Key and Clustering columns), the partitions are distributed across the nodes of the cluster
- The sequence in which columns appear reflect how the data is partitioned and the order of the data within the partitions
- Any clustering column(s) would determine the order in which the data is sorted within the partition